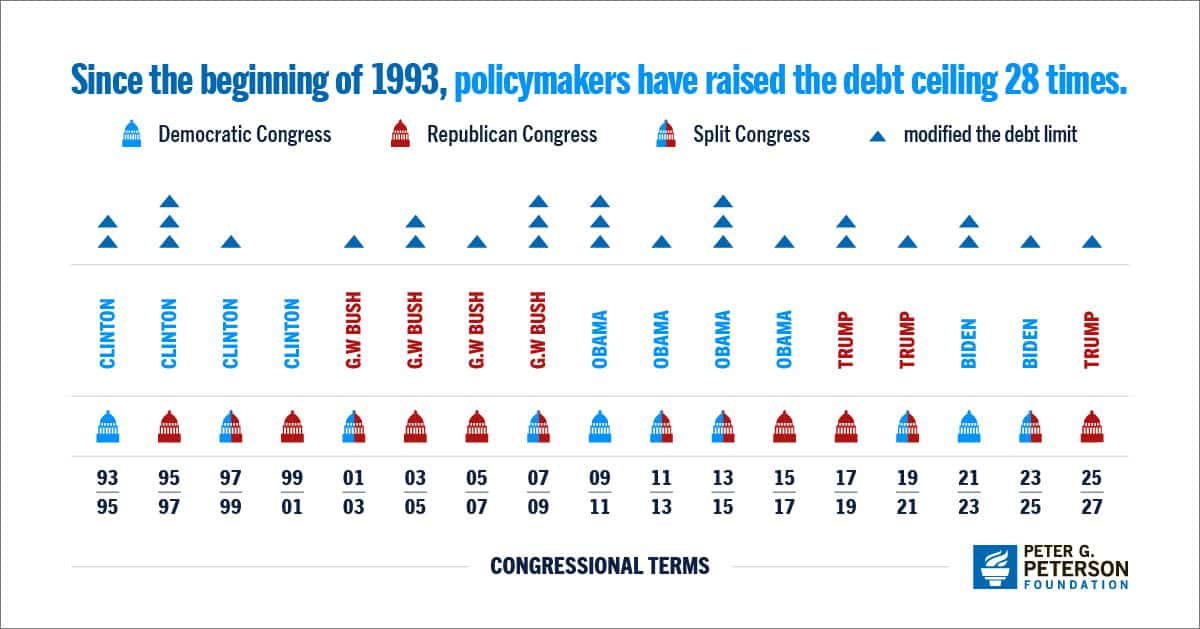
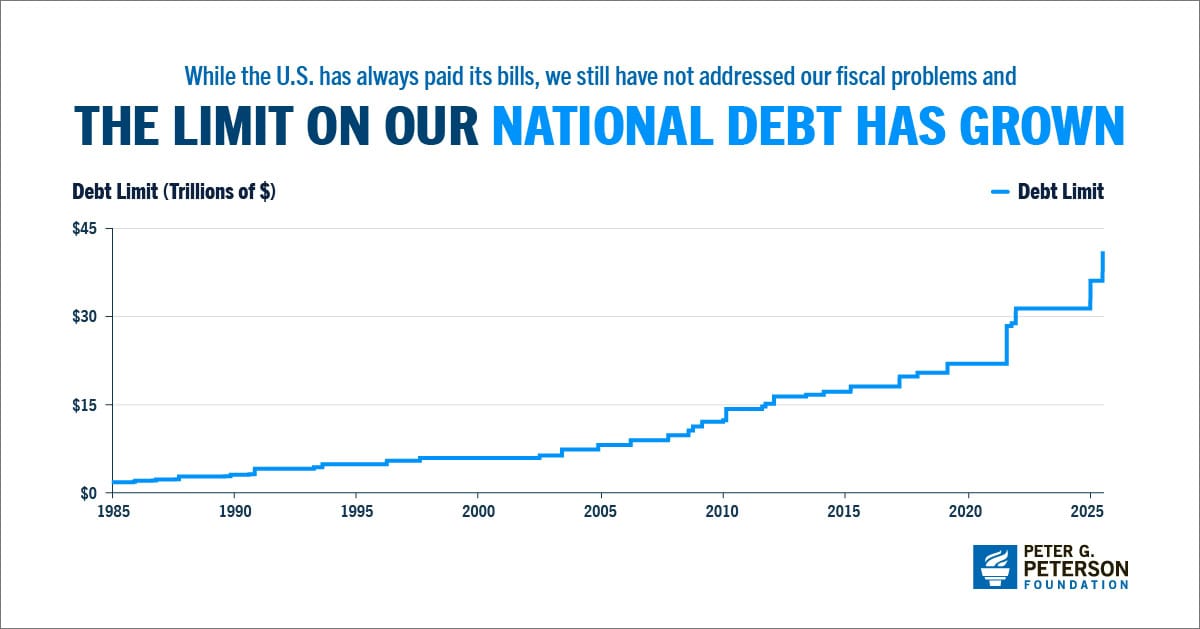
The debt ceiling, also known as the debt limit, is the maximum amount of money that the U.S. Treasury can borrow. Increasing the debt ceiling allows the Treasury to borrow funds to pay for government obligations that have already been incurred as the result of laws and budgets approved by the President and the Congress.
Legislation signed into law in July 2025 extends the debt ceiling by $5 trillion — from $36.1 to $41.1 trillion.
Why is understanding the debt ceiling important and what are the implications for our economy and our fiscal condition? The infographic below explains. For more details, see our analysis on the debt ceiling.

Feel free to share this infographic on Twitter.
Further Reading
Lawmakers are Running Out of Time to Fix Social Security
Without reform, Social Security could be depleted as early as 2032, with automatic cuts for beneficiaries.
Budget Basics: How Does Social Security Work?
Social Security is the largest single program in the federal budget and typically makes up one-fifth of total federal spending.
How Did the One Big Beautiful Bill Act Affect Federal Spending?
Overall, the OBBBA adds significantly to the nation’s debt, but the act contains net spending cuts that lessen that impact.