The outlook for the federal budget has worsened considerably since last year, according to a new report by the Congressional Budget Office (CBO). The sharp deterioration in the budget outlook stems from the large spending and tax bill that was enacted in December 2015, which increases deficits considerably over the next 10 years and beyond. CBO’s latest report highlights that America’s fiscal policy over the long-term remains unsustainable and threatens our future economy.
The CBO report finds that:
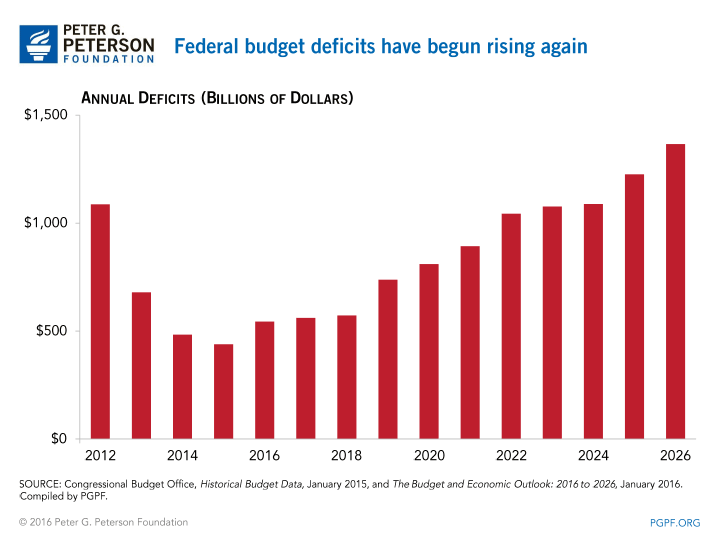
1. The federal budget has a structural mismatch between spending and revenues, which will lead to rising deficits over the next decade and beyond. Federal deficits will exceed the $1 trillion mark in 2022 and deficits will total $9.4 trillion over the next 10 years.
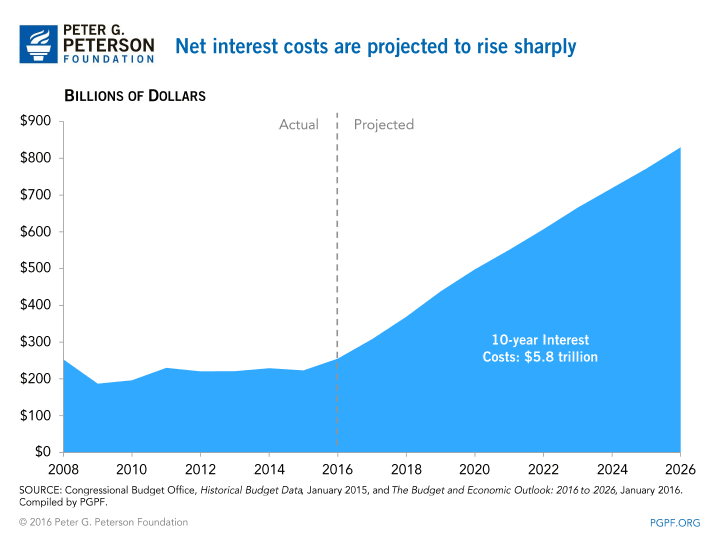
2. Interest costs on the debt will climb sharply. Over the next 10 years, net interest costs will total $5.8 trillion.
3. Federal debt is projected to rise to 86 percent of gross domestic product (GDP) in 2026 — double its 50-year average and higher than at any point since just after WWII. Debt levels thereafter will climb sharply as a share of GDP.
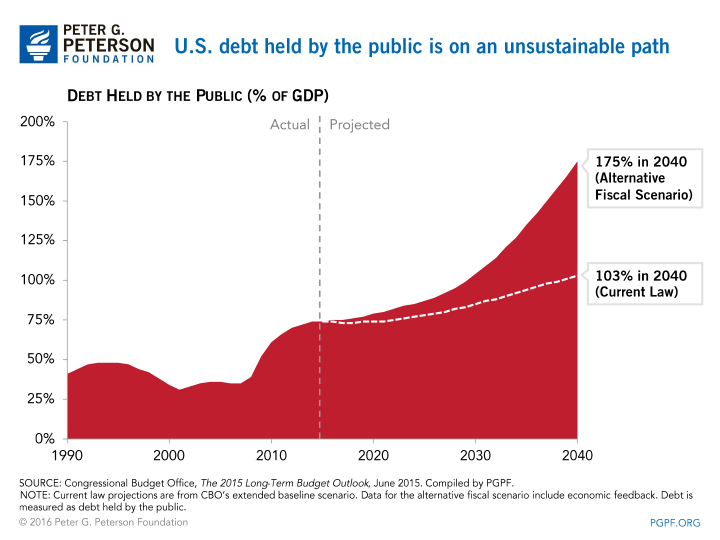
Image credit: Getty Images
Further Reading
Top 10 Reasons Why the National Debt Matters
At $38 trillion and rising, the national debt threatens America’s economic future. Here are the top ten reasons why the national debt matters.
What Is the National Debt Costing Us?
Programs that millions of Americans depend on and care about may be feeling a squeeze from interest costs on our high and rising national debt.
Interest Costs on the National Debt Are Reaching All-Time Highs
The most recent CBO projections confirm once again that America’s fiscal outlook is on an unsustainable path — increasingly driven by higher interest costs.


