The economic impact of the coronavirus has been profound, but it has not been felt equally by all demographic groups.
The official unemployment rate in November 2020 was 6.7 percent, which represents 11 million people unemployed out of a civilian labor force of 160 million individuals. In addition to those counted as officially unemployed, there were 6.7 million people who indicated that they wanted full-time work but were only able to secure part-time work.
Supplemental data from the monthly report on unemployment from the Bureau of Labor Statistics provides additional detail and insights on the individuals who became unemployed between the week of March 15, when states began to issue stay-at-home orders in response to the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic, and the week of November 8, when the most recent employment data were collected.
Key takeaways:
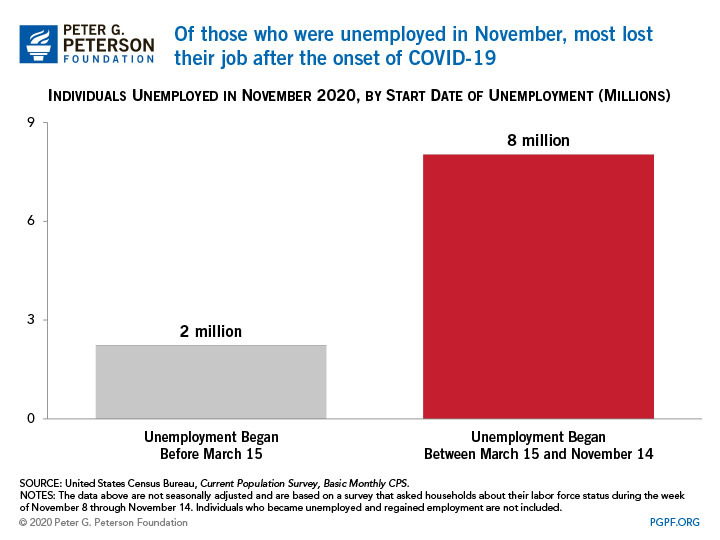
1. The vast majority of Americans who were unemployed in November became unemployed during the pandemic.
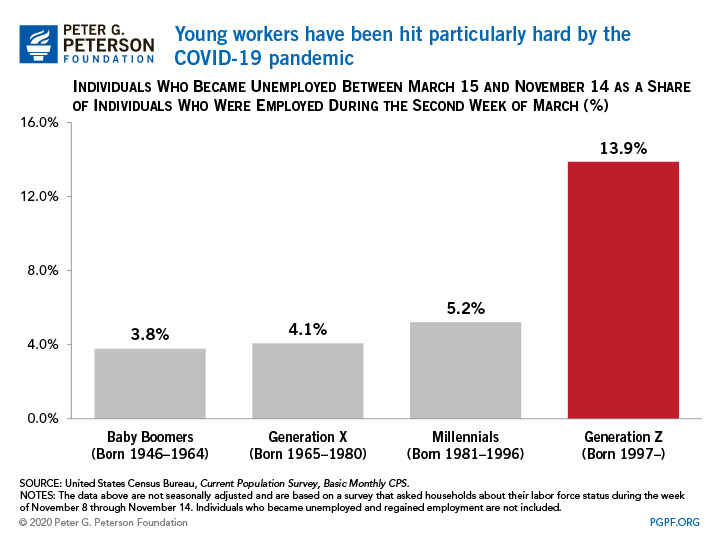
2. The nation’s youngest workers have been hit hardest by job losses during the coronavirus pandemic.
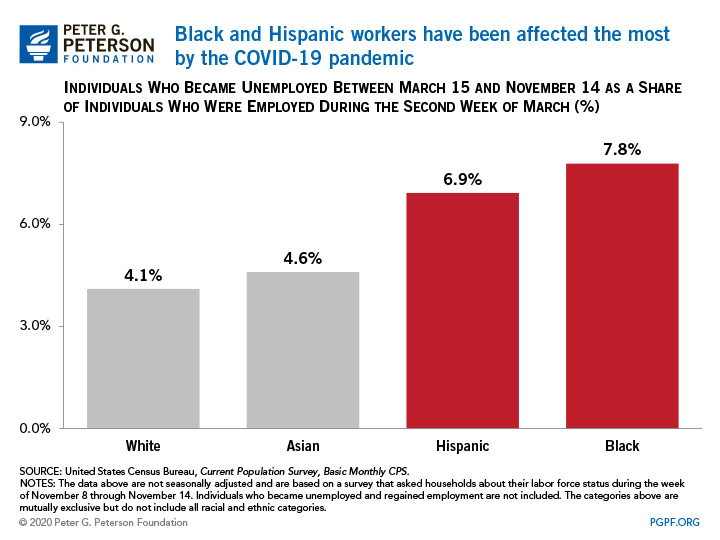
3. Non-white workers have suffered some of the worst effects that COVID-19 has had on the labor market.
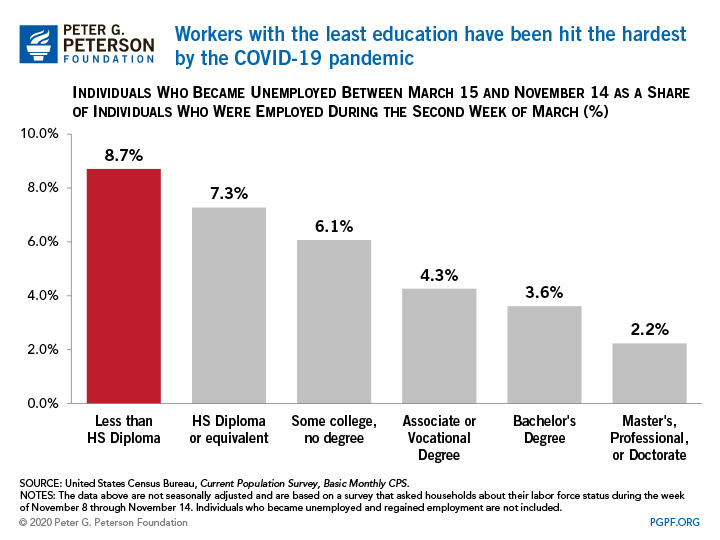
4. Workers with lower levels of education have had a particularly rough time in the labor market during the coronavirus pandemic.
The data reported recently by BLS also confirms earlier research about the disparity in unemployment among various groups. For example, the Pew Research Center pointed out that Hispanic men and women faced particularly sharp increases in unemployment rates during the early months of the pandemic.
Much of the current labor market data are based on a survey that faces data collection challenges resulting from the pandemic, and which asked respondents about their employment during the second week of November. As a result, those data only tell part of the story of how the coronavirus pandemic has affected the labor market. Nonetheless, the data available thus far provide a valuable look into where the labor market is heading, and who might need assistance moving forward.
Image credit: Photo by Spencer Platt/Getty Images
Further Reading
What’s the Difference Between the Trade Deficit and Budget Deficit?
The terms “budget deficit” and “trade deficit” can be conflated, but they are distinct measurements of important fiscal and economic concepts.
The Fed Reduced the Short-Term Rate Again, but Interest Costs Remain High
High interest rates on U.S. Treasury securities increase the federal government’s borrowing costs.
What Types of Securities Does the Treasury Issue?
Learn about the different types of Treasury securities issued to the public as well as trends in interest rates and maturity terms.


