Peter G. Peterson Foundation July "Fiscal Confidence Index" Finds Voters Maintain Highly Negative Attitudes on the National Debt
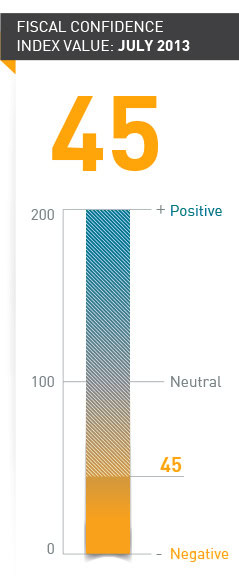
The July 2013 Fiscal Confidence Index, Modeled after the Consumer Confidence Index, is 45 (100 is Neutral); Eighth Straight Month of Strongly Negative Public Sentiment
With Key Fiscal Milestones in Coming Months, 84% of Voters Believe the President and Congress Should Spend More Time Addressing the Debt
NEW YORK — Americans maintain strongly negative attitudes about our nation’s fiscal challenges, according to the Peter G. Peterson Foundation’s latest Fiscal Confidence Index, a monthly measure of public attitudes about the nation’s long-term debt and the efforts elected leaders are making to address the problem.
The July 2013 Fiscal Confidence Index, modeled after the Consumer Confidence Index, is 45 (100 is neutral), indicating strongly negative public sentiment about America’s fiscal situation. The overall July index is unchanged from the June reading, which was also 45. Sentiment has remained consistently negative since the launch of the Fiscal Confidence Index in December 2012.
“For the eighth straight month, the Fiscal Confidence Index shows that voters have deep concerns about our nation’s long-term debt,” said Michael A. Peterson, President and COO of the Peterson Foundation. “As we approach the August recess for Congress, major questions about our long-term fiscal future remain unanswered and voters are rightly skeptical. This fall, instead of governing by crisis, our nation’s leaders will have the opportunity to show true leadership by using the upcoming debates over the debt ceiling and the budget to both put our economy on a prosperous path and ensure our nation’s long-term fiscal health.”
The Fiscal Confidence Index measures public opinion about the national debt by asking six questions in three key areas:
- CONCERN: Level of concern and views about the direction of the national debt.
- PRIORITY: How high a priority addressing the debt should be for elected leaders.
- EXPECTATIONS: Expectations about whether the debt situation will get better or worse in the next few years.
The survey results from these three areas are weighted equally and averaged to produce the Fiscal Confidence Index value. The Fiscal Confidence Index, like the Consumer Confidence Index, is indexed on a scale of 0 to 200, with a neutral midpoint of 100. A reading above 100 indicates positive sentiment. A reading below 100 indicates negative sentiment.
Fiscal Confidence Index Key Data Points:
- The July 2013 Fiscal Confidence Index value is 45. A score of 100 is neutral. Values below 100 show negative sentiment, while values above 100 show positive sentiment. (June’s value was 45. May’s value was 47.)
- The current Fiscal Confidence Index score for CONCERN about the debt is 38, indicating strong concern about the debt. The score for debt as a PRIORITY that leaders must address is 22, indicating that Americans want elected leaders to make addressing long-term debt a high priority. The score for EXPECTATIONS about progress on the debt over the next few years is 74, indicating pessimism about the direction of long-term fiscal policy in the next few years. The Fiscal Confidence Index of 45 is the average of these three sub-category scores.
- The July score held even with the June score. Scores have remained consistently negative since the launch of the Index in December 2012.
- For a description of the complete methodology, see the Appendix below.
The Peter G. Peterson Foundation commissioned the poll by the Global Strategy Group to survey public opinion on the national debt. The nationwide poll included 1,004 U.S. registered voters, surveyed by telephone between July 22 and July 24, 2013. The poll has a margin of error of +/- 3.1%. The poll examined voters’ opinions on the national debt, political leadership, and America’s fiscal and economic health.
Detailed poll results can be found online at: www.pgpf.org/what-we-are-doing/education-and-awareness/fiscal-confidence-index
About the Peter G. Peterson Foundation
The Peter G. Peterson Foundation is a nonprofit, nonpartisan organization established by Pete Peterson — businessman, philanthropist, and former U.S. Secretary of Commerce. The Foundation is dedicated to increasing public awareness of the nature and urgency of key long-term fiscal challenges threatening America’s future and to accelerating action on them. To address these challenges successfully, we work to bring Americans together to find and implement sensible, long-term solutions that transcend age, party lines and ideological divides in order to achieve real results. To learn more, please visit www.pgpf.org.
APPENDIX: Fiscal Confidence Index Methodology and Questions
- The Fiscal Confidence Index is released monthly by the Peter G. Peterson Foundation.
- The Fiscal Confidence Index value is based on six questions in three categories.
- As is done with the Consumer Confidence Index, the first step in calculating the Fiscal Confidence Index is determining the “Relative Value” for each question. This calculation is made by taking the positive response for each question and dividing it by the sum of the positive and negative responses. Each question was asked on a four-point scale, and answers were weighted according to intensity, with the strongest responses counting twice as much as the middle responses (“much” better or worse answers count twice as heavily as “somewhat” better or worse answers).
- The scores for the Concern, Priority, and Expectations categories are determined by averaging the scores derived from the two questions in each category.
- The Fiscal Confidence Index value is converted from the Relative Value to place it on a scale on which 100 indicates equal positive and negative sentiment, while values below 100 indicate negative sentiment and values above 100 indicate positive sentiment.
- The Peter G. Peterson Foundation commissioned the poll by the Global Strategy Group to survey public opinion on the national debt. The nationwide poll included 1,004 U.S. registered voters, surveyed by telephone between July 22 and July 24, 2013. The poll has a margin of error of +/- 3.1%. The poll examined voters’ opinions on the national debt, political leadership, and America’s fiscal and economic health.
- The questions are as follows:
| CONCERN (38) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thinking about our national debt over the last few years, would you say your level of concern has increased or decreased? ◊ Is that a lot or just a little? |
July 2013 | June 2013 | May 2013 | |
| Increased a lot | 53% | 55% | 54% | |
| Increased a little | 21% | 20% | 19% | |
| Decreased a little | 8% | 7% | 8% | |
| Decreased a lot | 4% | 6% | 4% | |
| (No change) | 13% | 10% | 14% | |
| (Don’t Know/Refused) | 1% | 2% | 1% | |
| INCREASED (NET) | 74% | 75% | 73% | |
| DECREASED (NET) | 12% | 13% | 12% | |
| When it comes to addressing our national debt, would you say things in the United States are heading in the right direction or do you think things are off on the wrong track? ◊ Do you feel that way strongly or just somewhat? |
July 2013 | June 2013 | May 2013 | |
| Right direction-Strongly | 11% | 9% | 13% | |
| Right direction-Somewhat | 18% | 19% | 17% | |
| Wrong track-Somewhat | 16% | 16% | 16% | |
| Wrong track-Strongly | 46% | 44% | 44% | |
| (Neither/Mixed) | 4% | 7% | 6% | |
| (Don’t Know/Refused) | 5% | 4% | 4% | |
| RIGHT DIRECTION (NET) | 29% | 28% | 30% | |
| WRONG TRACK (NET) | 62% | 60% | 60% | |
| PRIORITY (22) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Some people say that addressing the national debt should be among the President and Congress’ top 3 priorities. Do you agree or disagree? ◊ Do you feel that way strongly or just somewhat? |
July 2013 | June 2013 | May 2013 | |
| Strongly agree | 60% | 61% | 61% | |
| Somewhat agree | 20% | 22% | 20% | |
| Somewhat disagree | 7% | 6% | 8% | |
| Strongly disagree | 8% | 8% | 7% | |
| (Don’t Know/Refused) | 5% | 3% | 4% | |
| AGREE (NET) | 80% | 84% | 81% | |
| DISAGREE (NET) | 14% | 14% | 15% | |
| And when it comes to our national debt, do you think it is an issue that the President and Congress should spend more time addressing or less time addressing? ◊ Would you say a lot (more or less) time or just a little? |
July 2013 | June 2013 | May 2013 | |
| A lot more time | 64% | 63% | 65% | |
| A little more time | 20% | 20% | 17% | |
| A little less time | 5% | 5% | 6% | |
| A lot less time | 4% | 4% | 5% | |
| (The same amount of time) | 4% | 4% | 4% | |
| (Don’t Know/Refused) | 4% | 4% | 3% | |
| MORE TIME (NET) | 84% | 84% | 82% | |
| LESS TIME (NET) | 9% | 8% | 11% | |
| EXPECTATIONS (74) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| And thinking about our national debt over the next few years, do you expect the problem to get better or worse? ◊ Is that much (better or worse) or just somewhat (better or worse)? |
July 2013 | June 2013 | May 2013 | |
| Much better | 18% | 10% | 10% | |
| Somewhat better | 20% | 18% | 20% | |
| Somewhat worse | 25% | 27% | 26% | |
| Much worse | 37% | 36% | 36% | |
| (No change) | 4% | 3% | 3% | |
| (Don’t know/Refused) | 6% | 5% | 4% | |
| BETTER (NET) | 28% | 28% | 31% | |
| WORSE (NET) | 62% | 63% | 63% | |
| And when it comes to our national debt, are you optimistic or pessimistic that the United States will be able to make progress on our national debt over the next few years? ◊ Would you say you are very (optimistic or pessimistic) or just somewhat? |
July 2013 | June 2013 | May 2013 | |
| Very optimistic | 20% | 17% | 20% | |
| Somewhat optimistic | 28% | 32% | 29% | |
| Somewhat pessimistic | 18% | 16% | 17% | |
| Very pessimistic | 29% | 29% | 29% | |
| (Neither/Mixed) | 3% | 3% | 3% | |
| (Don’t Know/Refused) | 3% | 3% | 2% | |
| OPTIMISTIC (NET) | 47% | 49% | 49% | |
| PESSIMISTIC (NET) | 46% | 46% | 46% | |
Further Reading
Lawmakers are Running Out of Time to Fix Social Security
Without reform, Social Security could be depleted as early as 2032, with automatic cuts for beneficiaries.
What Is the National Debt Costing Us?
Programs that millions of Americans depend on and care about may be feeling a squeeze from interest costs on our high and rising national debt.
Interest Costs on the National Debt Are Reaching All-Time Highs
The most recent CBO projections confirm once again that America’s fiscal outlook is on an unsustainable path — increasingly driven by higher interest costs.