After months of negotiations, the House of Representatives has passed a major budget reconciliation bill that aims to accomplish numerous priorities of the Biden Administration. The Build Back Better Act, which is now in the hands of the Senate, proposes $2.2 trillion in new spending and tax cuts and would offset nearly $2 trillion of that total, based on estimates from the Congressional Budget Office and calculations by the Committee for a Responsible Federal Budget (CRFB).1
The Build Back Better Act includes spending on a wide variety of policy areas. If enacted, the legislation would provide benefits for many lower-income households, take steps to address climate change, and make other social investments.
CRFB’s analysis indicates that the legislation is mostly paid for on paper; however, the package relies on budget timing gimmicks that could potentially hide the true cost of the proposed programs and create year-to-year uncertainty for millions of Americans affected by the legislation. Several of the proposed programs in the package would expire within the 10-year budget window. For example, the extensions of the increased Child Tax Credit and the expanded Earned Income Tax Credit both expire after just one year. If lawmakers choose to extend them again in the future, the true cost of the package could be much higher over the next 10 years (unless future extensions are also offset).
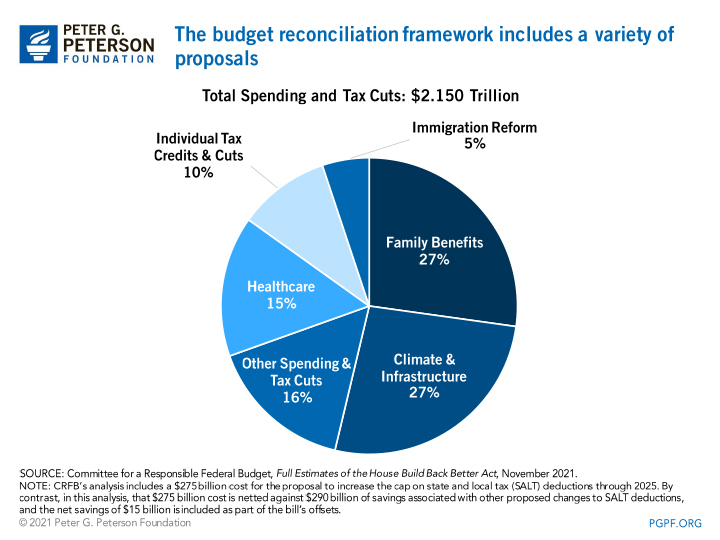
CRFB calculates that the package would be mostly paid for with offsets that are primarily focused on tax increases for the wealthy and large corporations.
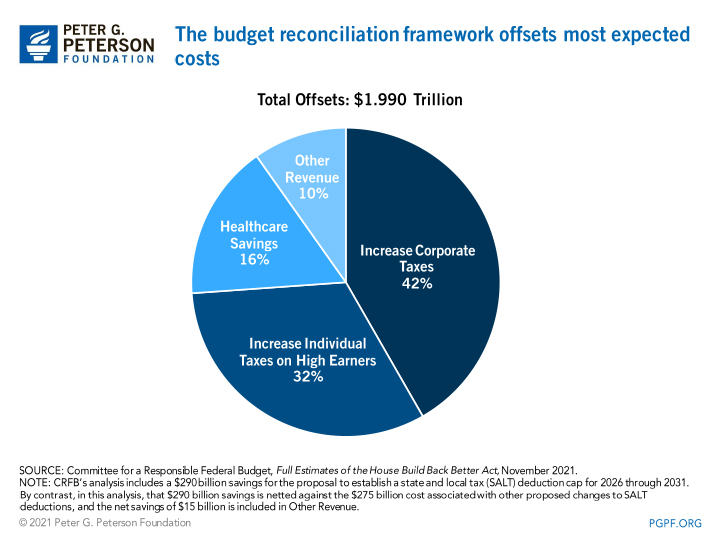
lawmakers still have an important opportunity to further improve this legislation by fully paying for their priorities in a durable and sustainable way, avoiding budget gimmicks, and providing more certainty for the economy, budget, and society.
Photo by Paul Morigi/Getty Images
Further Reading
Should We Eliminate the Social Security Tax Cap?
There have been a number of proposals to increase, eliminate, or otherwise adjust the payroll tax cap as a way to shore up Social Security’s finances.
No Taxes on Tips Will Drive Deficits Higher
Here’s how this new, temporary deduction will affect federal revenues, budget deficits, and tax equity.
Three Reasons Why Assuming Sustained 3% Growth is a Budget Gimmick
GDP growth of 3 percent is significantly higher than independent, nonpartisan estimates and historically difficult to achieve.


