You are here
Federal Deficit and Debt: November 2019
Every month the U.S. Treasury releases data on the federal budget, including the current deficit. The following contains budget data for November 2019, which was the second month of fiscal year (FY) 2020.
Current Federal Deficit
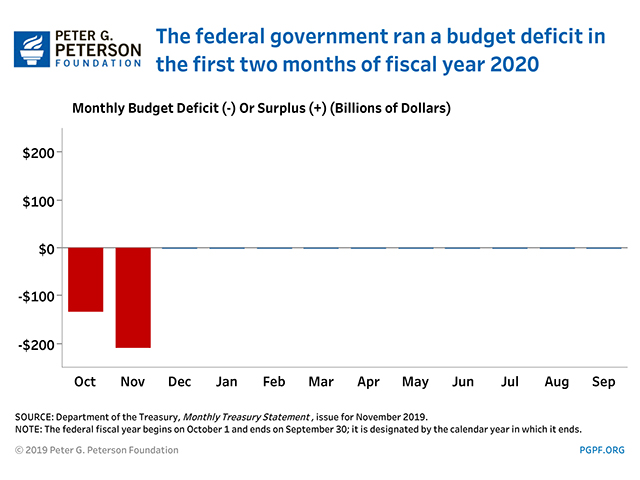
- Federal Budget Deficit for November 2019: $209 billion
- Federal Budget Deficit for November 2018: $205 billion
The deficit for November 2019 was $4 billion larger than that recorded in November 2018. In both years, certain federal payments were shifted into November because December 1st fell on a weekend. Without such timing shifts, the November 2019 deficit would have been about the same as the November 2018 deficit.
Cumulative Federal Deficit
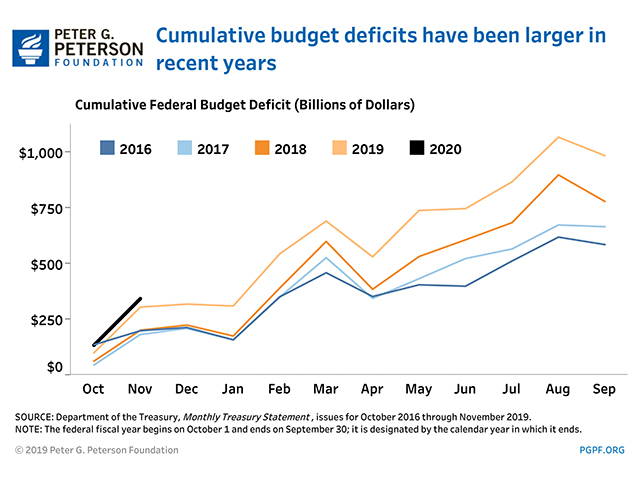
- Cumulative FY20 Deficit through November 2019: $343 billion
- Cumulative Budget Deficit over same period in FY19: $305 billion
The cumulative deficit through the first two months of FY20 was $38 billion larger than it was through the first two months of FY19. If the shifts of payments into November of both years were excluded, the cumulative FY20 deficit would have been $34 billion larger.
The increase in the cumulative deficit reflects a $50 billion increase in outlays slightly offset by a $12 billion increase in revenues.
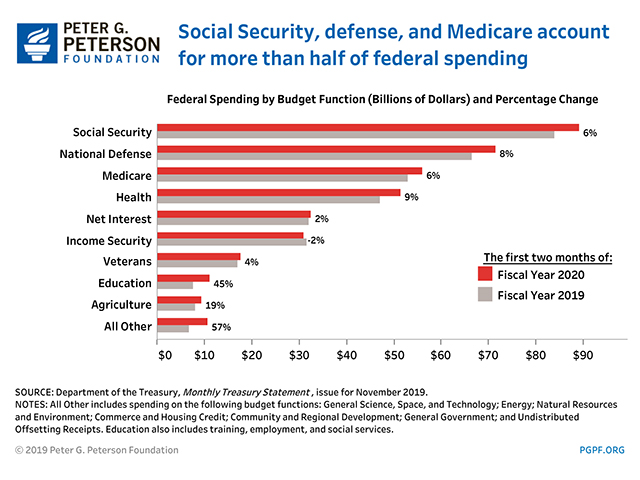
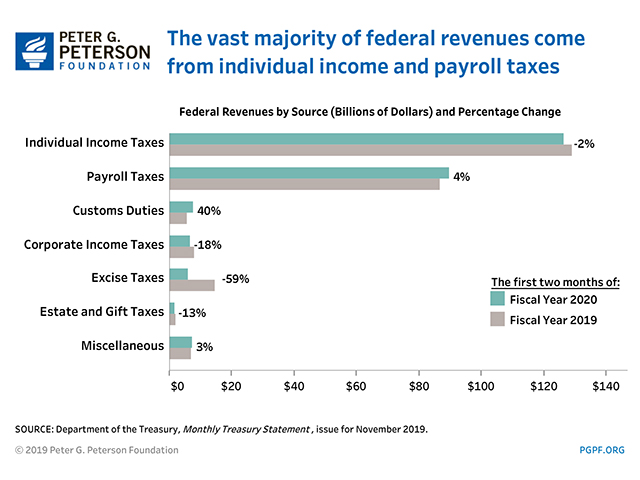
National Debt
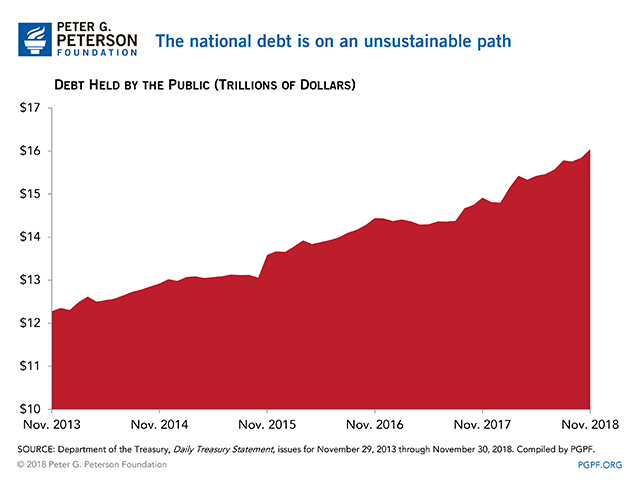
- Debt Held by the Public at the End of November 2019: $17.1 trillion
- Debt Held by the Public through November 2018: $16.0 trillion
While the deficit varies from month to month, and may even decline some months — for example, in April when taxpayers are submitting their personal income taxes — debt and deficits are on an unsustainable upward trajectory. The CBO projects that national debt could rise to about 140 percent of gross domestic product by 2049. That level of debt would far exceed the 50-year historical average of approximately 40% of GDP.
Why are such high levels of debt so concerning? There are many reasons that Americans should be concerned about the rising national debt — particularly if you are concerned about economic growth, investments in our nation’s future, and preservation of our social safety net.
